
Source: TECH NEW TODAY
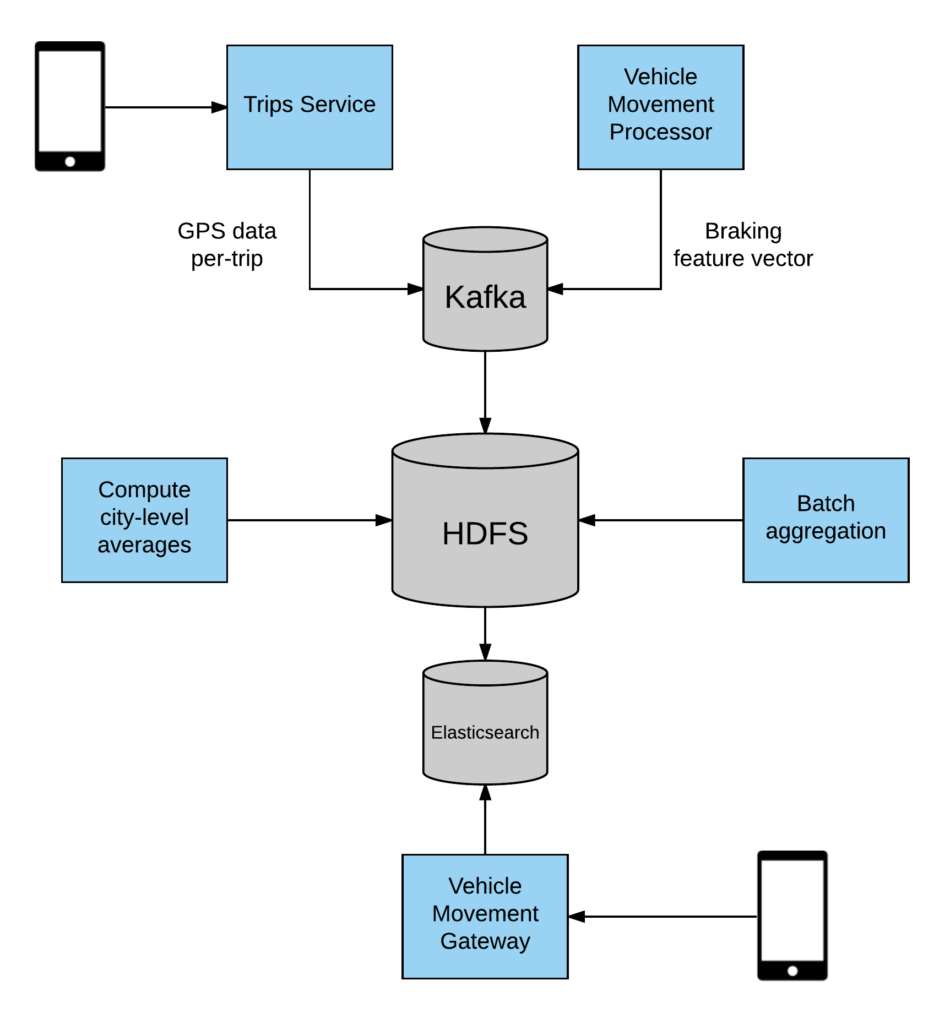 The article entitled “How Uber Engineering Increases Safe Driving With Telematics” by Beinstein and Sumers (2016) provides insight on Uber’s utilization of telematic data to improve road safety and eradicate unsafe driving habits. Under the company’s mobile architecture, Global Positioning System (GPS) information from each trip is processed under Trip Services. This is combined with the information gathered via Uber’s Vehicle Movement Processor, which analyses key indicators including harsh braking and sudden acceleration, which will complement and enhance the credibility of the telematics data obtained from the drivers. Combining the information from Uber’s Trip Services Vehicle Movement Processor, the resultant data will then be processed under Apache’s distributed streaming platform, Kafka, before they are committed to long-term storage under the HADOOP Distributed File System (HDFS). Beinstein and Sumers (2016) also highlighted Uber’s use of various computational software, including Apache Hive and Apache Spark, to compute and derive telematic statistics such as “daily city-level averages for hard brakes.” After being analysed, these data will be indexed under the Elasticsearch cluster and made available via an Application Programming Interface (API) for developers.
The article entitled “How Uber Engineering Increases Safe Driving With Telematics” by Beinstein and Sumers (2016) provides insight on Uber’s utilization of telematic data to improve road safety and eradicate unsafe driving habits. Under the company’s mobile architecture, Global Positioning System (GPS) information from each trip is processed under Trip Services. This is combined with the information gathered via Uber’s Vehicle Movement Processor, which analyses key indicators including harsh braking and sudden acceleration, which will complement and enhance the credibility of the telematics data obtained from the drivers. Combining the information from Uber’s Trip Services Vehicle Movement Processor, the resultant data will then be processed under Apache’s distributed streaming platform, Kafka, before they are committed to long-term storage under the HADOOP Distributed File System (HDFS). Beinstein and Sumers (2016) also highlighted Uber’s use of various computational software, including Apache Hive and Apache Spark, to compute and derive telematic statistics such as “daily city-level averages for hard brakes.” After being analysed, these data will be indexed under the Elasticsearch cluster and made available via an Application Programming Interface (API) for developers.Uber’s embracement and effective deployment of innovative technology has ushered in fundamental changes to the traditional transportation and ride-hailing industry and “adds to the safety of the service far more than any government regulation could” (Shaffer, 2017). In contrast to traditional taxi companies in Singapore, Uber has employed numerous key safety features including analysing of sentiment data, collecting of vehicle telematics data, and utilizing of sensors on drivers’ devices to detect and predict behaviours of drivers (Kashyap, 2017).
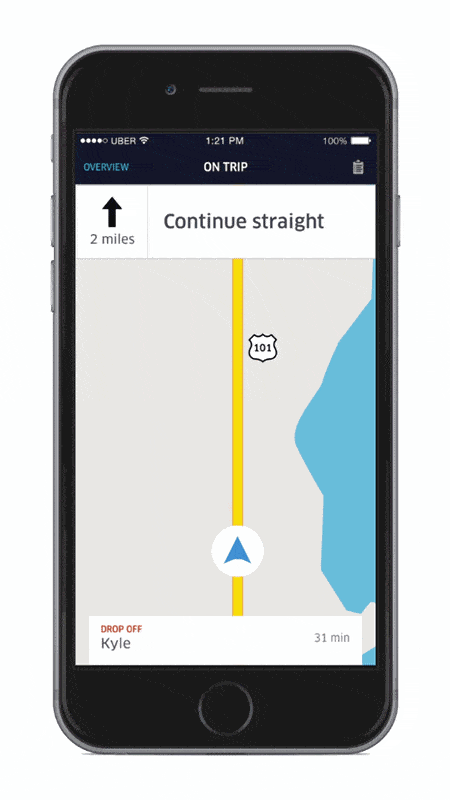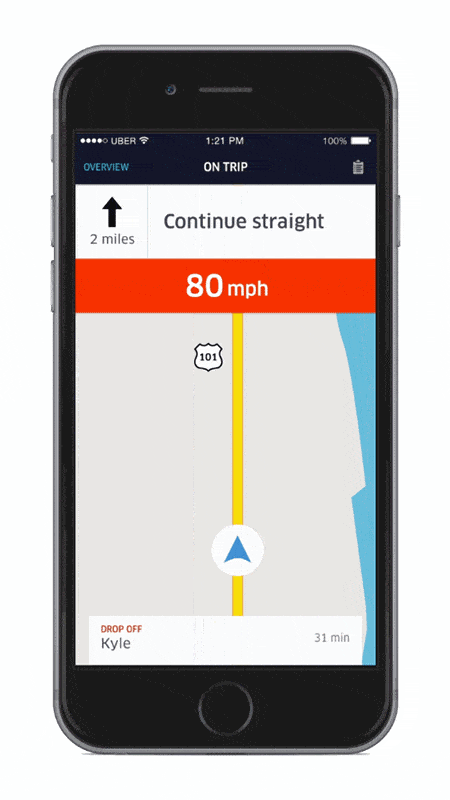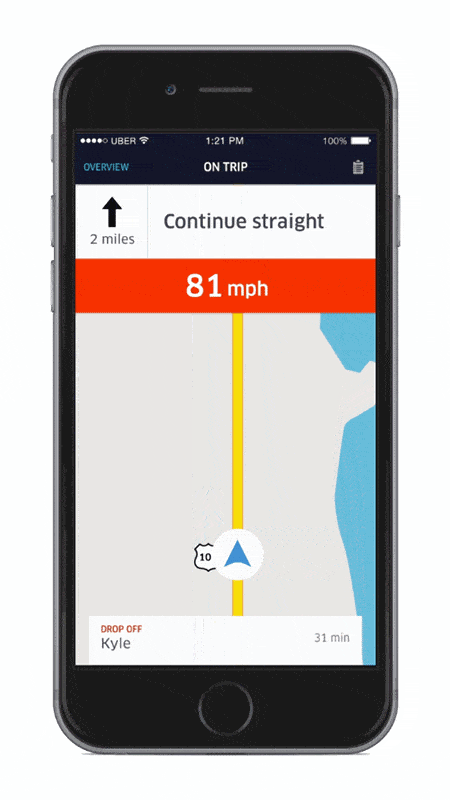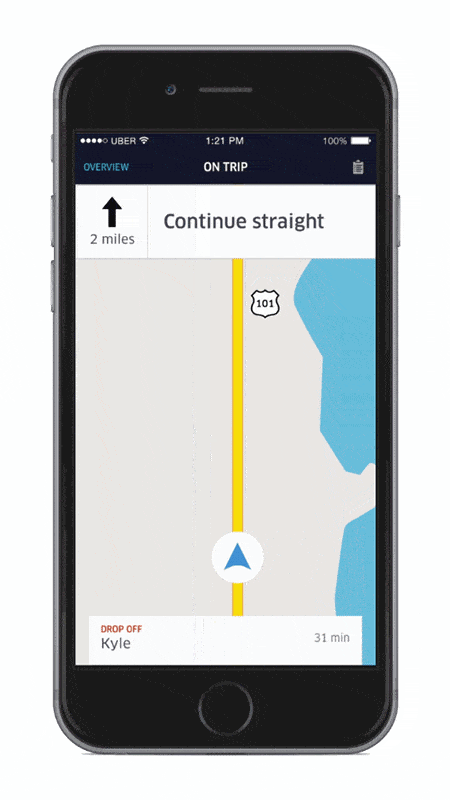
In fact, Uber has also entered into partnership with various non-profit organizations such as the Governor’s Highway Safety Association and MADD (Sheehey-Church, 2016) to introduce numerous safety pilots to its consumers. Some examples include personalized travel reports for drivers, speed displays and other safety reminders pertaining to the drivers’ use of the app.
In addition, to sleeve out drivers who continuously demonstrate poor driving skills or exhibits poor driving habits, a bi-directional rating framework (known as the Uber Star Rating) is adopted. As mentioned by Isaac (2014), both drivers and riders will be prompted to provide ratings to each other after each trip. Under this rating system, driver who received a collective rating of less than 4.6 out of 5.0 will be notified to be at risk of being “deactivated”; which encourages drivers to consistently improve and correct bad driving habits.
In conclusion, the emergence and evolution of Uber has revolutionized the ride-hailing industry while providing commuters with a safer alternative to the traditional taxis. In addition, Uber’s utilization of telematics data and innovative technology, such as speed tracking via GPS technology and the use of a rating system, further illustrates Uber’s long-term commitment to promote safe driving through leveraging of telematics technologies
References (APA):
Beinstein, A., & Sumers, T. (2017). How Uber Engineering Increases Safe Driving with Telematics. Uber Engineering Blog. Retrieved October 02, 2017, from https://eng.uber.com/telematics/
Isaac, E. (2014). Disruptive Innovation: Risk-Shifting and Precarity in the Age of Uber. Retrieved October 01, 2017, from https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/0d90/07be68160ee0c27e2abb5e10f92a42075e66.pdf.
Kashyap, S. (2017), How Uber is harnessing technology to ensure safe rides. Retrieved October 07, 2017, from https://yourstory.com/2017/09/uber-harnessing-technology-ensure-safe-rides
Shaffer, S. (2017), Uber, Lyft are safer than cabs. Retrieved October 07, 2017, from http://www.baltimoresun.com/news/opinion/readersrespond/bs-ed-uber-lyft-letter-20170103-story.html
Sheehey-Church, C. (2016). New App Features and Data Show How Uber Can Improve Safety on the Road. Retrieved October 12, 2017, from https://www.uber.com/newsroom/safety-on-the-road-july-2016
No comments:
Write comments